Oracle Fusion
Industry: Finance
11 August, 2025The CBUAE is the supervisory and regulatory authority of the banking and insurance sector.
The CBUAE promotes financial and monetary stability, efficiency and resilience in the financial system, and the protection of consumers through effective supervision that supports economic growth for the benefit of the UAE and its people.
Objectives
- Enable Automation in Gaps of Oracle Fusion: Automate updates in Oracle Fusion Payables and Financials where no APIs or FBDI templates are available.
- Improve Process Efficiency: Eliminate manual operations for daily and repetitive tasks like currency rate updates and invoice field adjustments.
- Enhance Accuracy and Timeliness: Ensure error-free and timely processing of business data through automation and validation.
Business Challenges
- Lack of Standard Interfaces: The Landed Cost Reference field in Oracle Fusion Payables cannot be updated using REST APIs or FBDI templates, creating a gap in automation.
- Manual Data Entry Risk: Manual entry of daily currency rates or invoice references is time-consuming and prone to human error, impacting data reliability and audit compliance.
- No API Access for External Data Source: The Central Bank UAE publishes currency rates in web table format only, without API endpoints, making automation difficult through traditional methods.
- Dependency on Functional Users: Both use cases require frequent involvement of users for updating the UI manually, which is not scalable.
- Time Sensitivity: Currency exchange rates must be uploaded daily before business transactions. Any delay leads to incorrect or failed financial postings.
Implementation
Use Case 1: Updating Landed Cost Reference in Payables Invoices
Challenge:
Oracle Fusion Payables does not provide native support to update the Landed Cost Reference (LCR) field through public REST APIs or FBDI templates. This creates a significant limitation when automating invoice-related operations where LCR values are mandatory for downstream processing or reporting.
End-to-End Solution:
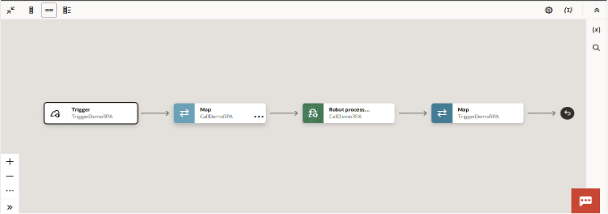
To overcome these limitations, an integrated automation is designed using Oracle Integration Cloud (OIC) and Oracle Robotic Process Automation (RPA), ensuring seamless invoice creation and post-submission LCR updates.
Step-by-Step Workflow
-
Invoice Creation in Source System:
- Invoices are generated without LCR details due to system limitations.
- These records contain basic invoice header and line data.
-
Invoice Submission via REST API:
- The source system sends invoice data to OIC through an exposed REST interface.
- OIC receives and transforms the payload as required.
-
Invoice Creation in Oracle Fusion ERP:
- OIC invokes the Fusion Payables REST API to create invoices in Oracle Fusion.
- Since the LCR fields are not supported in the API, they are intentionally left blank.
-
Trigger RPA for UI-Based LCR Update:
- Once the invoice is successfully created in Fusion, OIC triggers the RPA bot.
- Trigger payload includes key data such as:
- Invoice Number
- Line Number
- LCR Reference Value
-
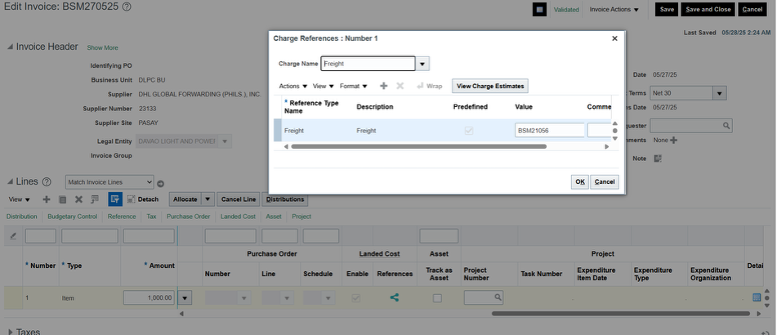
RPA Performs UI-Based Update:
- RPA logs into the Oracle Fusion Payables UI as a user would.
- It navigates to Manage Invoices, searches for the invoice, and updates the Landed Cost Reference at the line level via the UI.
-
Success/Error Logging & Notifications:
- RPA logs the result (success/failure) for each invoice line.
- The status is sent back to OIC.
- OIC optionally notifies the source system or business users via email or webhook.
Use Case 2: Daily Currency Rate Automation from CBUAE
Challenge:
Oracle Fusion Financials supports automated currency rate loading through FBDI templates, but the source for accurate exchange rates — the Central Bank of the UAE (CBUAE) — does not offer a web service or API. Instead, it publishes daily rates as a web-based table, requiring manual download and upload of data into Oracle Fusion.
This manual process introduces risk, delays, and compliance issues, especially in high-volume, multi-currency environments.
End-to-End Solution:
An automated integration using Oracle RPA and Oracle Integration Cloud (OIC) was implemented to extract currency data from CBUAE daily and load it into Oracle Fusion Financials via the supported Daily Rates FBDI format.

Step-by-Step Workflow
-
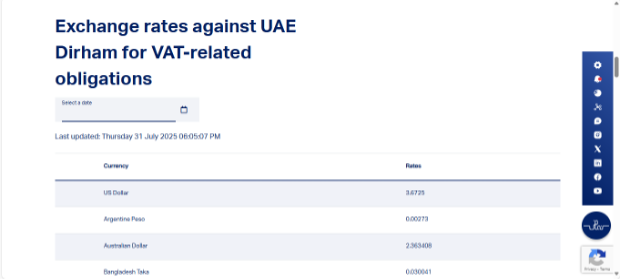
RPA Bot Scrapes Exchange Rates from CBUAE Website:
- At a scheduled time each day, the RPA bot opens the CBUAE website.
- It scrapes the web table containing the latest daily currency rates.
- The data includes:
- Currency Code (e.g., USD, EUR)
- Rate Value
-
Format to FBDI Template:
- The bot formats the extracted data into the standard Oracle FBDI template for Daily Rates:
- Uses proper headers (From Currency, To Currency, Conversion Rate, Conversion Date, etc.)
- Saves the data as a CSV file and compresses it into a .zip.
-
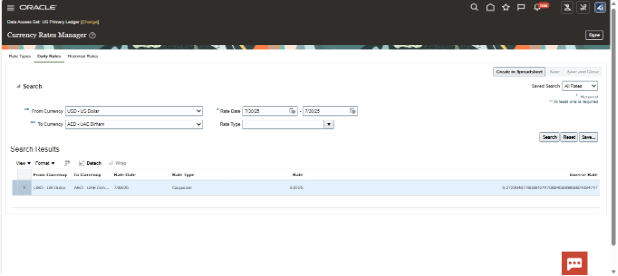
OIC Picks Up and Processes the File:
- OIC picks the generated .zip file from an intermediate location (e.g., FTP, Stage, or local shared path).
- Uploads it to Oracle UCM using the File Adapter.
- Triggers the “Load Interface File for Import” ESS job.
Benefits Achieved
- Reduction in Manual Effort: Replaced repeated daily and invoice-specific tasks with automated bots and flows.
- Improved Data Accuracy and Audit Readiness: All operations logged and validated, supporting audit and compliance requirements.
- Scalable and Reusable Framework: The RPA + OIC approach can be extended to other non-API-supported gaps in Oracle Fusion.
- Operational Efficiency: Reduced turnaround time for FX updates and invoice corrections from hours to minutes.
- Business Continuity: Daily updates no longer dependent on availability of functional users.
Challenges
- UI Fragility: RPA bots break with UI changes and need regular maintenance.
- Lower Scalability: RPA is slower and less scalable compared to API-based integrations.
- Manual Error Recovery: Some RPA errors require human intervention.
- Monitoring Complexity: Dual monitoring needed across RPA and OIC layers.
- Security Risks: RPA credentials must be tightly managed to prevent breaches.
Conclusion
By combining RPA and OIC, critical business functions were successfully automated even in the absence of native APIs or file-based loaders. This hybrid approach can be reused across other similar gaps in Oracle Fusion and offers a flexible, reliable automation framework—despite some maintainability and monitoring overhead.



