Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG): Empowering AI with Real-Time Knowledge
Key Highlights
- RAG revolutionizes AI by enabling real-time retrieval of external data, ensuring responses are accurate and up-to-date.
- Reduces AI hallucinations by grounding outputs in verifiable, external sources, enhancing reliability.
- Diverse RAG architectures—Vector, Graph, and Hybrid—offer tailored solutions for varied data types and use cases.
Introduction
What if your AI assistant could not only chat like a friend but also research like a scholar—pulling the latest insights from a secure, curated digital library in milliseconds? In a world where information evolves rapidly and privacy concerns are paramount, traditional generative AI models often fall short, relying on static training data that may be outdated, incomplete, or uncontrolled. Enter Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG)—a breakthrough that transforms AI from a clever conversationalist into a responsible, knowledge-driven powerhouse. By combining real-time, privacy-aware data retrieval with natural language generation, RAG ensures AI delivers accurate, trustworthy, and contextually relevant answers. Let’s explore how RAG bridges the gap between knowledge and generation—making AI not just smart, but secure and wise.
Unlocking Deeper Knowledge: What is RAG?
Imagine a brilliant scholar who, instead of relying solely on memory, has instant access to a global library of up-to-date resources. That’s RAG in a nutshell. Retrieval-Augmented Generation enhances Large Language Models (LLMs) by enabling them to fetch external data in real time, augmenting their responses with fresh, relevant information. Unlike traditional LLMs, which are limited to their pre-trained knowledge—like a book with a fixed number of pages—RAG acts as a digital librarian, scouring external sources to provide answers that are both conversational and deeply informed.
In a world where modern LLMs can perform web searches and access vast amounts of real-time data, maintaining data privacy becomes more critical than ever. For instance, consider asking an AI about privacy laws or internal company policies. Without RAG, the model might access or hallucinate sensitive or irrelevant information. With RAG, however, responses are grounded in a controlled, curated set of documents—ensuring that only approved, privacy-compliant data is used. This makes RAG essential for applications where trust, security, and confidentiality are non-negotiable
Why is this a game-changer for AI?
- Tackling AI Hallucinations: Traditional LLMs can sometimes generate plausible but incorrect information, known as “hallucinations.” RAG minimizes this by anchoring responses in verified external data, ensuring factual accuracy. For example, instead of guessing a company’s latest earnings, RAG retrieves the most recent financial reports.
- Delivering Real-Time Insights: RAG keeps AI current by accessing live data sources, such as news feeds or scientific journals. This is invaluable for dynamic fields like stock trading or public health, where outdated information can lead to costly mistakes.
- Building Trust: By citing traceable sources, RAG transforms AI into a reliable partner. Users can verify the data behind the answers, fostering confidence in AI-driven decisions.
The Inner Workings: How RAG Connects AI to the World’s Data
RAG’s magic lies in its seamless integration of retrieval and generation, executed through a three-stage process that empowers AI to tap into a constantly evolving knowledge base. Here’s how it works:
- The Intelligent Indexing Phase:
Before RAG can retrieve data, external sources—such as corporate documents, research archives, or web pages—must be prepared. These texts are broken into manageable chunks, each transformed into vector embeddings, numerical representations that capture the semantic meaning of the content. Think of embeddings as digital fingerprints that allow AI to understand not just words, but their context and relationships. These embeddings are stored in a vector database, optimized for rapid, meaning-based searches. For example, a company’s product manuals might be indexed to answer customer queries with pinpoint accuracy.
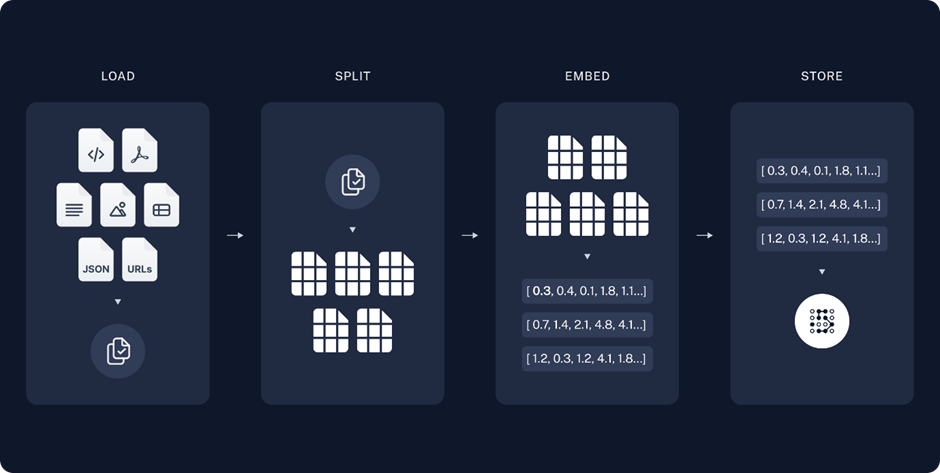
Source: https://python.langchain.com/docs/tutorials/rag/#setup
- The Dynamic Retrieval Phase:
When you ask a question, RAG converts your query into a vector embedding. This query embedding is then compared to the vector database, identifying the most semantically relevant chunks of information. Unlike keyword-based searches, RAG focuses on meaning, so asking “What’s the latest on AI ethics?” retrieves documents discussing recent ethical frameworks, even if they don’t use your exact phrasing. This phase ensures the AI pulls the most pertinent data in real time, whether from a company’s internal wiki or a public archive. - The Augmented Generation Phase:
With relevant data retrieved, RAG combines these chunks with your query to form an augmented prompt. This prompt is fed to the LLM, which weaves its pre-trained knowledge with the new context to generate a response. The result? Answers that are not only fluent but also precise, grounded in external data. For instance, a RAG-powered AI asked about a new drug’s efficacy might retrieve clinical trial data, ensuring its response is both scientifically accurate and conversational. This process happens in milliseconds, delivering insights that feel instant yet deeply informed.
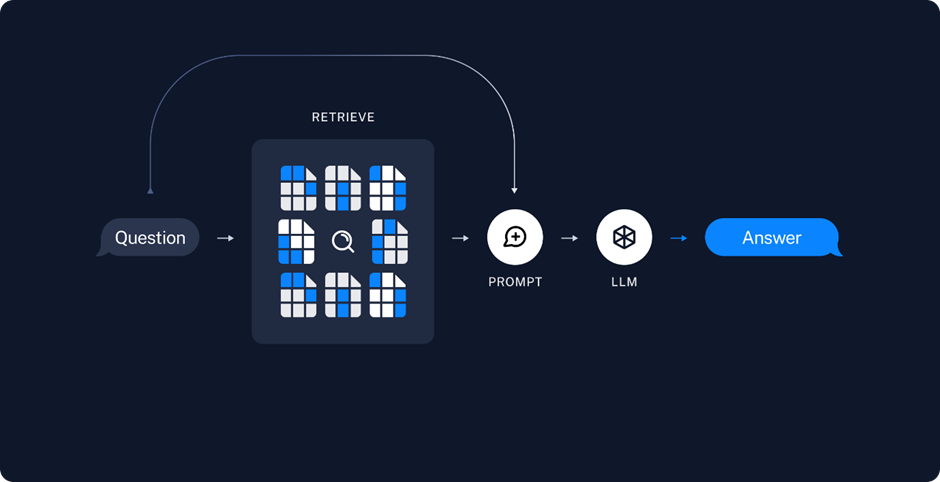
Source: https://python.langchain.com/docs/tutorials/rag/#setup
Diverse Approaches: Exploring RAG’s Architectural Varieties
RAG’s flexibility shines through its varied architectures, each designed to handle specific data types and use cases. Here’s a closer look at the three main types:
- Vectorized RAG:
The most common RAG approach, Vectorized RAG excels at semantic understanding. It converts text into vector embeddings, capturing the essence of content rather than relying on exact keyword matches. When a user asks a question, their query is transformed into a vector, and the system searches the vector database for the closest matches. This enables retrieval of relevant information even when phrasing differs. For example, asking “How does AI improve healthcare?” might retrieve documents on AI diagnostics, even if they use terms like “machine learning” or “patient outcomes.”
Strengths: Fast, scalable, and ideal for unstructured text like articles or reports.
Limitations: Struggles with explicit relationships (e.g., “Which company acquired another?”)
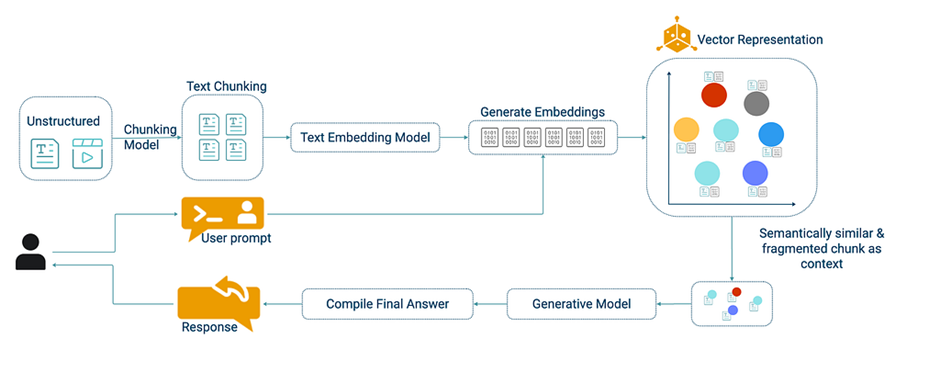
Source: https://neo4j.com/blog/developer/graphrag-and-agentic-architecture-with-neoconverse/
- Graph RAG (Knowledge Graph RAG):
Graph RAG leverages knowledge graphs, where data is structured as nodes (entities like people or places) and edges (relationships like “works for” or “located in”). This approach excels at multi-hop reasoning, answering complex questions that require connecting multiple pieces of information. For instance, asking “Who founded the company that acquired X in 2024?” involves navigating a graph to link founders, companies, and acquisitions.
Strengths: Reduces hallucinations by retrieving structured, factual data and offers explainable results by tracing the graph’s paths.
Limitations: High complexity in creating and maintaining graphs, requiring significant computational resources and expertise in data modeling. It’s less suited for unstructured, free-form text.
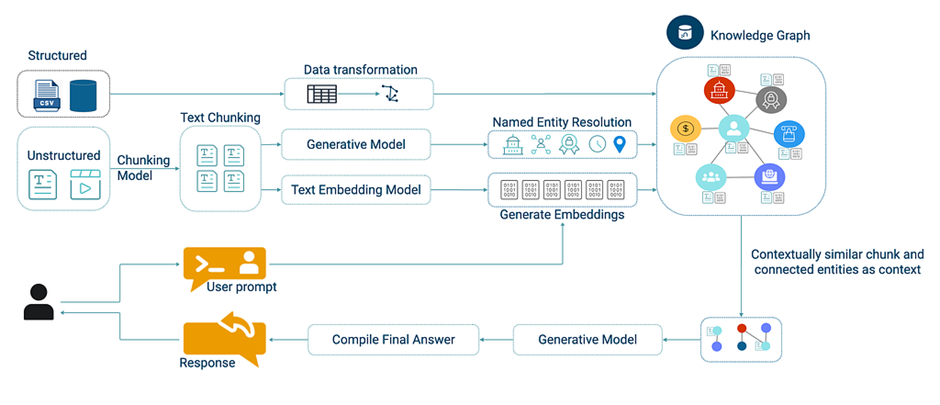
Source: https://neo4j.com/blog/developer/graphrag-and-agentic-architecture-with-neoconverse/
- Hybrid RAG:
Hybrid RAG combines the best of both worlds, blending Vectorized RAG’s semantic flexibility with Graph RAG’s relational precision. For example, a Hybrid RAG system might use vector search to identify relevant documents (e.g., news articles on a merger), then apply a knowledge graph to extract specific relationships (e.g., “Company A acquired Company B”). This dual approach maximizes accuracy and context, making it ideal for complex queries in domains like legal research or competitive analysis.
Strengths: Offers comprehensive, trustworthy answers by balancing semantic and relational data.
Limitations: Increased complexity and latency due to managing multiple databases and retrieval steps, demanding robust computational infrastructure.
Future Scope
RAG is more than a technological leap—it’s a foundation for the future of intelligent, reliable AI. By enabling LLMs to dynamically access external knowledge, RAG paves the way for systems that evolve with the world’s information. Future advancements may include smarter retrieval algorithms that prioritize context over raw similarity, seamless integration with diverse data formats (e.g., video or audio transcripts), and AI models that refine their retrieval strategies based on user feedback. For example, a RAG system could learn to prioritize peer-reviewed journals for scientific queries, enhancing precision over time.
As RAG matures, it will empower AI to tackle increasingly complex challenges, from personalized education to real-time market analysis. By delivering transparent, verifiable, and contextually rich insights, RAG is not just enhancing chatbots—it’s shaping a future where AI is a trusted partner in decision-making.
Summary
RAG transforms AI by bridging the gap between static training data and dynamic, real-world knowledge. Its three-stage process—indexing, retrieval, and generation—ensures answers are accurate, current, and trustworthy. With architectures like Vectorized, Graph, and Hybrid RAG, developers can tailor solutions to diverse data needs, from semantic searches to relational reasoning. As RAG evolves, it promises to make AI not just conversational, but genuinely insightful, paving the way for a future of reliable, knowledge-driven intelligence.
About the Author
S A Arvind Kumar Ponsingh – AI intern at 4i Apps working with the PD GEN AI team on GraphRAG, pioneering new ways to combine knowledge graphs and generative AI for smarter, more context-aware systems. Currently working on a smart PDF Q&A systems using Neo4j combining NLP with graph-based retrieval. With a background in AI & Data Science and past work in full-stack and BI tools, He shares thoughts on GenAI, RAG, and building AI systems that are not just powerful but explainable and grounded in real-world use cases.






